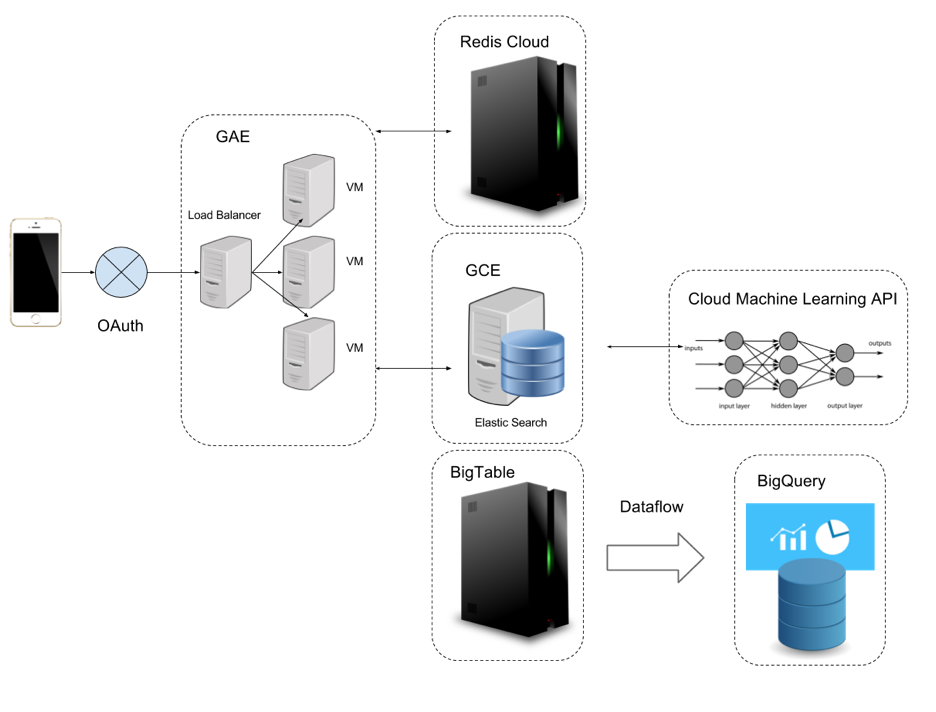
Project Introduction
Around: a Geo-index based social network
• Built a scalable web service in Go to handle posts and deployed to Google Cloud (GAE flex) for better scaling
• Utilized ElasticSearch (GCE) to provide geo-location based search functions such that users can search nearby posts within a distance (e.g. 200km)
• Used Google Dataflow to implement a daily dump of posts to BigQuery table for offline analysis
• Aggregated the data at the post level and user level to improve the keyword based spam detection (BigQuery)
constants.js1
2
3export const API_ROOT = 'https://around-75015.appspot.com';
export const TOKEN_KEY = 'TOKEN';
export const AUTH_PREFIX = 'Bearer';
Why we need to learn about Go?
Answer: server language for next generation (both computer friendly and developer friendly)
Who is using Golang
- Google (Creator), Uber, AirBnb
- Dropbox, Facebook, eBay, Heroku, Douban, Jingdong, Meituan
As opposed to Java, Go is compiled to machine code and is executed directly. Much like C.
Go example
1 | f, err := os.Open("filename.ext") |
Other benefits
- Multiple return values
- Multi-threading
- Go Routine
- Channels
- Has borrowed many good ideas from python
Python is really easy to break.
- Does not compile. You will never know it breaks until it breaks.
- Language is confusing.
- Good for testing and evaluation with many excellent machine learning libraries.
1 | a = set(['hippo']) |
Setup Local Environment (Go)
Make sure you have installed Go based on Prerequisite.
Mac Users (Windows User wait a minute)
Step 1.1.1 Open Terminal, enter
1 | go version |
It should show something like go version go1.10.2 darwin/amd64.
Step 1.1.2(Optional: GOPATH default to ~/go) In the same Terminal, enter
1 | mkdir ~/go |
In here we must not overwrite the bin of go, add
export PATH=$PATH:/usr/local/go/bin to .bash_profile and update zsh profile
Step 1.1.3 In the same Terminal, enter
1 | mkdir -p ~/Documents/Around/service |
Step 1.1.4 Type ‘a’ or ‘i’ and then copy a hello world program into main.go
1 | package main |
Step 1.1.5 Exit with :wq , in the terminal, type
1 | go run main.go |
You should be able to see the output of “Hello, world”
First Go program
First, we need to define some objects in a Go program to represent the data we store.
Step 1.3.1 let’s define the struct for post and location.
Encode json object (https://golang.org/pkg/encoding/json/)
1 | package main |
Step 1.3.2 Add one method handlerPost() after main() to handle Post.
1 | func main() { |
In here if you add rawString
json:"lat"after variable, it will parse it automatically
What does this method do? If user sends a http request with a body as
1 | { |
Then it will automatically construct a Post object named p and update its values to be p.User = “jack” and p.Message = “this is a message”
Fmt %s means string
Just one line of code to decode json object into go object. In comparison, if you do it in java.
1 | JSONObject venue = getVenue(event); |
Step 1.3.3 Replace main function to call handlerPost when started. Final version:
1 | import ( |
Step 1.3.5 Open your postman,
Choose ‘POST’, the url is http://localhost:8080/post, in the request body, enter1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8{
"user":"1111",
"message":"一生必去的100个地方",
"location":{
"lat":37.5,
"lon":-120.1
}
}
Click ‘Send’, you should be able to see a response with
1 | Post received: 一生必去的100个地方 |
Add another handler for search (called it handlerSearch), the request has a url pattern like
http://localhost:8080/search?lat=10.0&lon=20.0. Parse it and then print out the lat and lon.
Note: to get request parameters from url
1 | lat := r.URL.Query().Get("lat") |
Step 1.3.6 Answer1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14func main() {
fmt.Println("started-service")
http.HandleFunc("/post", handlerPost)
http.HandleFunc("/search", handlerSearch)
log.Fatal(http.ListenAndServe(":8080", nil))
}
func handlerSearch(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
fmt.Println("Received one request for search")
lat := r.URL.Query().Get("lat")
lon := r.URL.Query().Get("lon")
fmt.Fprintf(w, "Search received: %s %s", lat, lon)
}
Step 1.3.7 return a JSON object. Change handlerSearch to be
1 | Import ( |
在Go里面,变量必须得用到,不然会报错,除非用下划线做变量名
Step 1.3.8 Open Postman, url is http://localhost:8080/search?lat=10.0&lon=20.0&range=300 click send again. You should see something like this
1 | { |